This project is an example of a gRPC project using the Go language and the implementation client and server.
Protocol Buffer Go Plugin Installation
- install protocol buffer compiler in your local computer, For installation instructions, see Protocol Buffer Compiler Installation.
- Install Go plugin the protocol compiler:
Install the protocol compiler plugins for Go using the following commands:
$ go install google.golang.org/protobuf/cmd/protoc-gen-go@latest $ go install google.golang.org/grpc/cmd/protoc-gen-go-grpc@latestUpdate your PATH so that the protoc compiler can find the plugins:
$ export PATH="$PATH:$(go env GOPATH)/bin"
check detail in here. Great! We’re now ready to build our project.
Project Initialization
Let’s start by creating a new directory for our project:
mkdir go-simple-grpc && cd go-simple-grpc
initialize our Go module, install Go dependencies, and go vendoring:
go mod init github.com/adamnasrudin03/go-simple-grpc && go mod tidy && go mod vendor
Now from the root of the project, let’s create 3 subdirectories:
mkdir client server config data student
These 3 subdirectories will contain our Go client application, Go server application, and our student gRPC service. cd into the student directory and create a file called student.proto at the root of the project and add the following code:
syntax = "proto3";
package student;
option go_package = "github.com/adamnasrudin03/go-simpel-grpc/student";
service StudentService {
rpc GetStudentByEmail(Student) returns (Student) {}
}
message Student {
int32 id = 1;
string name = 2;
int32 age = 3;
string email = 4;
}
this code defines the structure of our gRPC service. we will use this structure in our client and server. We will use protoc command to generate our gRPC service and stub interface, run the following command:
protoc --go_out=paths=source_relative:. --go-grpc_out=paths=source_relative:. student/student.proto
this command will generate 2 files in student directory; student.pb.go and student_grpc.pb.go.
Configuration
create a file called config.go in the config directory with the following code:
package config
const (
DefaultPort = 1200
DefaultHost = "127.0.0.1"
ApiKey = "hello-grpc"
)
this code defines the configuration for our gRPC service.
Data
create a file called students.json in the data directory with the following code:
[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Adam",
"email": "adam@email.com",
"age": 30
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Nasrudin",
"email": "nasrudin@email.com",
"age": 40
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Adam Nasrudin",
"email": "adamnasrudin@email.com",
"age": 26
}
]
this code defines the data for our gRPC service.
Server Implementation
lets start with the server implementation by creating a file called main.go in the server directory, with the following code:
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"log"
"net"
"net/mail"
"os"
"sync"
"github.com/adamnasrudin03/go-simpel-grpc/config"
pb "github.com/adamnasrudin03/go-simpel-grpc/student"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"google.golang.org/grpc/codes"
"google.golang.org/grpc/metadata"
"google.golang.org/grpc/status"
)
type dataStudentServer struct {
pb.UnimplementedStudentServiceServer
mu sync.Mutex
students []*pb.Student
}
func IsValidEmail(email string) bool {
_, err := mail.ParseAddress(email)
return err == nil
}
func (s *dataStudentServer) GetStudentByEmail(ctx context.Context, in *pb.Student) (*pb.Student, error) {
s.mu.Lock()
defer s.mu.Unlock()
log.Printf("[GetStudentByEmail] incoming request : %v", in.Email)
if !IsValidEmail(in.Email) {
return nil, status.Errorf(codes.InvalidArgument, "Invalid email format")
}
for _, v := range s.students {
if v.Email == in.Email {
return v, nil
}
}
return nil, status.Errorf(codes.NotFound, "Data student not found")
}
func (s *dataStudentServer) loadData() {
data, err := os.ReadFile("data/students.json")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to read data: %v", err)
}
if err := json.Unmarshal(data, &s.students); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to load data: %v", err)
}
}
func newServer() *dataStudentServer {
s := dataStudentServer{}
s.loadData()
return &s
}
func isValidApiKey(keys []string) bool {
if len(keys) < 1 {
return false
}
for _, v := range keys {
if v == config.ApiKey {
return true
}
}
return false
}
// serverInterceptor intercepts gRPC calls and logs the request and response.
func serverInterceptor(ctx context.Context, req interface{}, info *grpc.UnaryServerInfo, handler grpc.UnaryHandler) (interface{}, error) {
log.Printf("[grpc-handler] incoming request: %v \n", info.FullMethod)
md, ok := metadata.FromIncomingContext(ctx)
if !ok {
log.Printf("[grpc-handler] Invalid request: %v \n", info.FullMethod)
return nil, status.Errorf(codes.InvalidArgument, "invalid request")
}
if !isValidApiKey(md["api-key"]) {
log.Printf("[grpc-handler] Invalid request: %v \n", info.FullMethod)
return nil, status.Errorf(codes.Unauthenticated, "Unauthorized")
}
resp, err := handler(ctx, req)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("[grpc-handler] Invalid request: %v err: %v \n", info.FullMethod, err)
return nil, err
}
log.Printf("[grpc-handler] Success request: %v \n", info.FullMethod)
return resp, nil
}
func main() {
add := fmt.Sprintf("%s:%d", config.DefaultHost, config.DefaultPort)
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", add)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to listen: %v", err)
}
grpcServer := grpc.NewServer(grpc.UnaryInterceptor(serverInterceptor))
pb.RegisterStudentServiceServer(grpcServer, newServer())
log.Printf("server listening at %v", lis.Addr())
if err := grpcServer.Serve(lis); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to serve: %v", err)
}
}
this code implementing the GetStudentByEmail method the service interface generate from the student.proto.
Client Implementation
Similar to the server implementation, we will create a file called main.go in the client directory with the following code:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"time"
"github.com/adamnasrudin03/go-simpel-grpc/config"
pb "github.com/adamnasrudin03/go-simpel-grpc/student"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"google.golang.org/grpc/credentials/insecure"
"google.golang.org/grpc/metadata"
)
func getDataStudentByEmail(ctx context.Context, client pb.StudentServiceClient, email string) {
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(ctx, 10*time.Second)
defer cancel()
student, err := client.GetStudentByEmail(ctx, &pb.Student{
Email: email,
})
if err != nil {
log.Printf("Failed to get student: (%v)", err)
return
}
log.Printf("Received: %v", student)
}
// main is the entry point of the client application.
//
// It does not take any arguments.
// It does not return anything.
func main() {
add := fmt.Sprintf("%s:%d", config.DefaultHost, config.DefaultPort)
// Create a connection to the server.
conn, err := grpc.Dial(add, grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials()))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to connect: %v", err)
}
defer conn.Close()
// Create a client for the StudentService.
client := pb.NewStudentServiceClient(conn)
// Add metadata to the context.
md := metadata.Pairs("api-key", config.ApiKey)
ctx := metadata.NewOutgoingContext(context.Background(), md)
// Get data student by email
fmt.Println("To exit press CTRL+C")
for {
email := ""
fmt.Print("Enter email: ")
fmt.Scanln(&email)
getDataStudentByEmail(ctx, client, email)
time.Sleep(1 * time.Second)
}
}
Installation packages and vendoring
go mod tidy && go mod vendor
Running project gRPC application
Run Server service
open terminal and run following command:
go run server/main.go
Run Client service
open new tab terminal and run following command:
go run client/main.go
Example output
Output Server in terminal 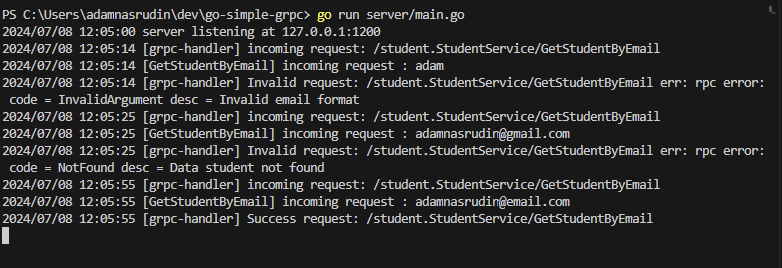 Output Client in terminal
Output Client in terminal 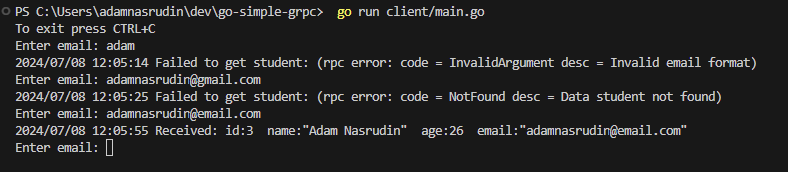 Output Client gRPC using Postman
Output Client gRPC using Postman 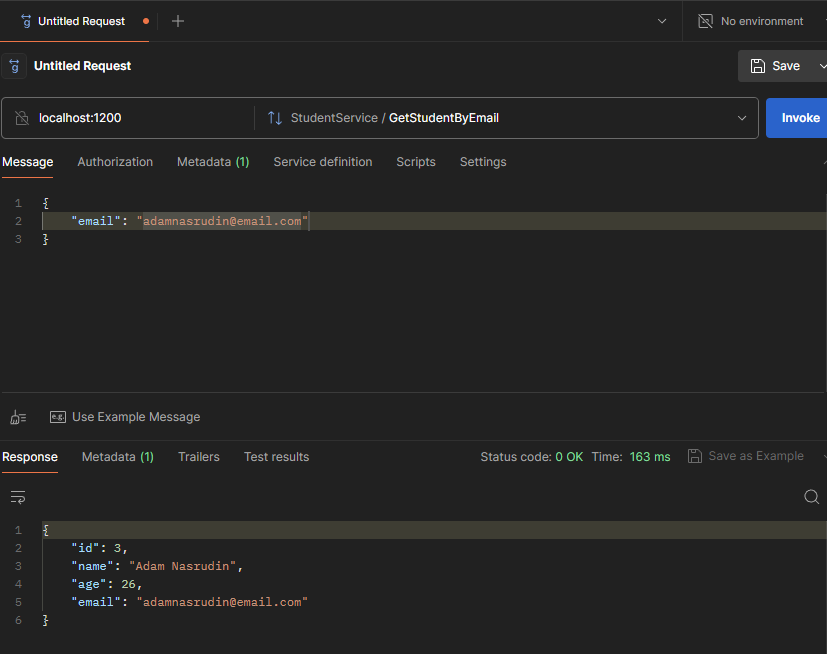
Output Client & Server in terminal 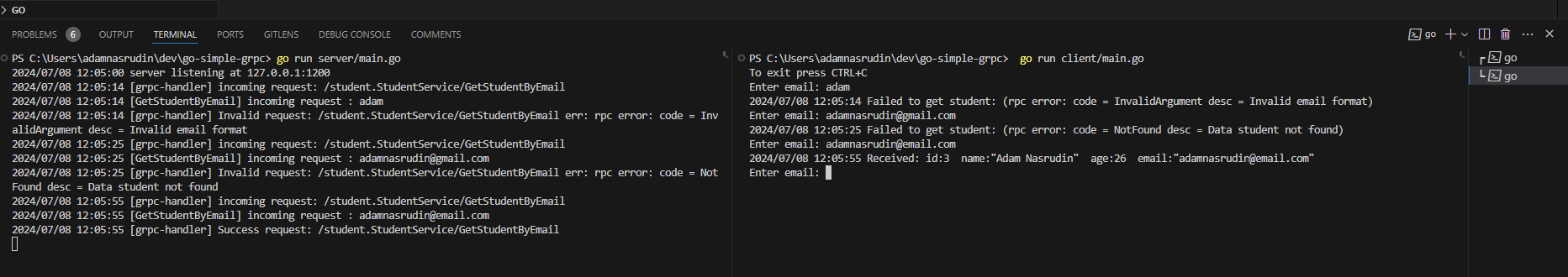 And there you have it! Your first gRPC server and client implementation.
And there you have it! Your first gRPC server and client implementation.
Conclusion
We have successfully implemented a gRPC service in Go. Now we can use the service in our application, detail code can be found here.